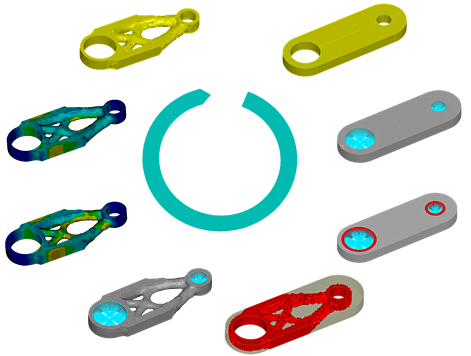
This article focuses on the possibilities for increasing innovation with Topology Optimization for Additive Manufactured Parts. Topology Optimization provides freedom to create unique structures that are a perfect fit for that given structural behaviour.
Deviation In estimation of Structural performance for 3D-printed Products
As the quality is going up, and costs for 3D printed parts are going down, more and more companies are adopting 3D printing in plastics and metals, not only for nice mock-ups and visual prototypes, but also for short-series produced parts. This brings a nice challenge to the development loop, because this means that products that are structurally loaded parts, should be validated someway, to make sure the structural performance of the 3D printed parts is as expected. Simply assuming isotropic material behaviour suddenly appears to be an assumption which is too much off, to say anything about the structural behaviour.
For plastic 3d printed parts, depending on the technology used, that means that most of the time, the products will fail at the transition of the layers at how the product is build-up, particularly at bending loadings that are perpendicular to the build-up direction.
For steel 3d printed parts, the printing process itself is contributing to the deviation of the accuracy, since heat is added due to the laser melting process. Also residual stresses are brought into the product by this thermal process and cooling down of the product.
More on how to accurately estimate the structural behaviour of 3D printed parts by taking into account the production process, will be covered in our Simuleon blog later this year.
How to Utilize the Design Freedom for 3d Printed Parts Under Structural Loading?
Most of you will acknowledge that 3D printing has less demands on the produce-ability of the actual part. So how do we design a 3D printed part specifically tailored for a given loading and boundary conditions? Luckily this is not depending on the creativeness of the average mechanical engineer, because if you would use known techniques, you most likely end up with parts that are square, circular or a combination of those shapes. This is where Topology Optimization comes in.
What is Topology Optimization?
Topology Optimization is a mathematical approach that optimizes material layout within a given design space, for a given set of loads and boundary conditions such that the resulting layout meets a prescribed set of performance targets. Using topology optimization, engineers can find the best concept design that meets the design requirements. Source Wikipedia.
Simuleon provides SIMULIA Tosca software in Belgium, Netherlands and Luxemburg , which is Topology Optimization Technology that can be used with many commercial FEA software, and of course SIMULIA Abaqus as well. And to add to this; Topology Optimization can’t be used without FEA software, since the FEA software brings the structural knowledge to the equations.
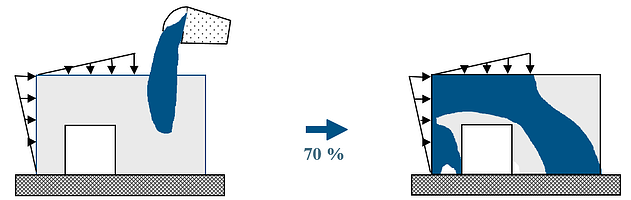
Topology Optimization is the non-parameter based optimization technique which removes material from the unloaded areas of the part, and creates structures that guide the load in the structure to the applied boundary conditions. With this technique you can create shapes that are an optimal fit for that given loading and boundary conditions. Topology Optimization can be used for Structural Analysis as well as CFD Analysis.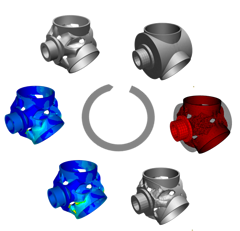
Some examples for Structural Topology Optimization:
- Maximize stiffness with volume constraint
- Maximize stiffness with frequency constraints
- Minimize displacement with volume constraint
- Minimize volume with displacement constraint
- Minimize reaction or internal force
- Maximize first eigenfrequencies
- Maximize the band gap around an eigenfrequency
- Restrict difference between two displacements
Lattice Structures to Dramatically Reduce Weight Even More Whilst Remaining Stiffness and Structural Performance
As the software industry and Dassault Systemes is rapidly picking up new trends, we see a large interest in the creation of Lattice Structures. These Lattice Structures are a logical follow-up on the model that was optimized with Tosca Topology Optimization to create even more weight reduction. So the optimized structure, which is normally still solid inside, can now be even reduced in its weight by the application of Lattice Structures. These structures are little beam-structures that are created on the sides of the mesh elements, which ideally are also directed in the loading direction or path. These techniques even provide more dramatic weight reductions, whilst remaining stiffness and structural performance. This technology is expected to be included in SIMULIA Tosca 2016 which will be released end of this year/begin of 2016.
Please view the interesting video below from Boeing with more information about lattice structures in general.

So in Summary, How Does Topology Optimization Contribute to Innovation for Additive Manufactured Products?
By applying clever techniques that create unique structures which are the best fit within the given boundary conditions, loadings and restrictions, the most innovative products and structures can be created. All the unnecessary bandwidth and excessive material is removed, and since FEA is already in the loop, the need for large numbers of physical prototypes has also been reduced at the same time.
Are you interested in applying these techniques to your products, designed for Additive Manufacturing?